Personalized mRNA Therapy Shows Promise in Rett Syndrome
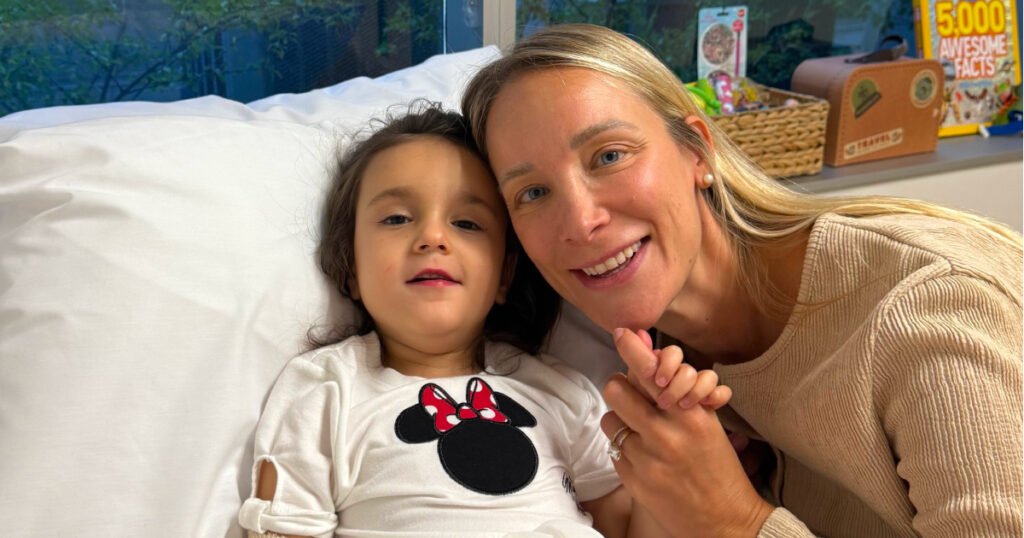
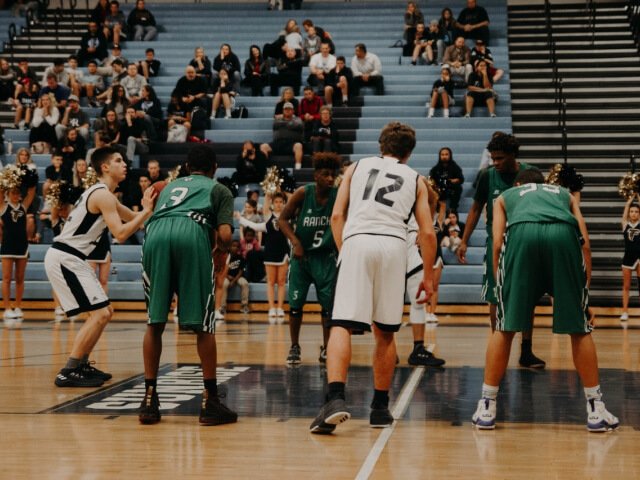
Recently, Grann Pharmaceuticals announced the development of a personalized experimental treatment, RTT-1 (Eleanor), for a young girl named Eleanor Elnekaveh, who has Rett Syndrome. This marks a significant step forward in the world of individualized medicine for rare neurological disorders. What is Rett Syndrome? Rett Syndrome is a severe, progressive neurodevelopmental disorder that primarily affects […]
Personalized mRNA Therapy Shows Promise in Rett Syndrome Read More »